“Breast disease” is a broad term covering a wide spectrum of benign and malignant conditions affecting the breast.
📌 Classification of Breast Diseases
1. Congenital / Developmental
- Polymastia (extra breast tissue)
- Polythelia (supernumerary nipple)
- Amastia, hypomastia, macromastia
- Inverted nipple
2. Inflammatory / Infective
- Acute mastitis (common in lactating women)
- Breast abscess (lactational / non-lactational, periductal)
- Tuberculous mastitis
- Fungal infections
3. Benign Breast Disorders
- Fibrocystic disease / Fibrocystic changes (lumpiness, pain, nodularity)
- Fibroadenoma (common benign tumor in young women)
- Phyllodes tumor (can be benign or malignant)
- Breast cysts
- Fat necrosis
- Duct ectasia
- Intraductal papilloma (may cause bloody nipple discharge)
- Gynecomastia (in males)
4. Breast Malignancies
- Carcinoma of the breast (most common female cancer worldwide)
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (most common)
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
- Inflammatory breast carcinoma
- Paget’s disease of the nipple
Risk factors:
- early menarche,
- late menopause,
- nulliparity,
- family history (BRCA1/2),
- obesity,
- radiation exposure.
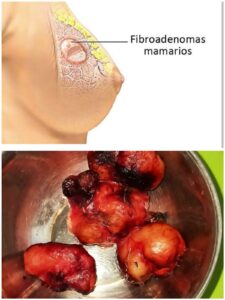
🔎 Clinical Features
- Lump in the breast (painless, hard, irregular → suspicious of malignancy).
- Pain, tenderness (common in benign diseases).
- Nipple discharge (serous, bloody, purulent).
- Nipple retraction, ulceration, skin changes (“peau d’orange”).
- Axillary lump (lymph node involvement).
- Systemic symptoms in advanced cancer (weight loss, bone pain, etc.).
🧪 Diagnostic Approach
1. Triple Assessment (gold standard):
- Clinical examination
- Imaging → Mammography, Ultrasound, MRI (in selected cases)
- Pathology → FNAC, core needle biopsy, excisional biopsy
2. Blood tests, hormone receptor status (ER, PR, HER2/neu) in carcinoma.
⚕️ Management
Benign lesions
- Reassurance, follow-up.
- Excision if symptomatic, enlarging, or suspicious.
Infective conditions
- Antibiotics, abscess drainage, good breast care.
Breast cancer
- Surgery: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy + axillary clearance) or mastectomy.
- Adjuvant therapy:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Hormonal therapy (tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors if ER/PR positive)
- Targeted therapy (trastuzumab for HER2-positive)
⚠️ Complications of Breast Diseases
- Cosmetic deformity, disfigurement.
- Recurrent abscess or infection.
- Infertility (secondary to treatment).
- Metastasis and mortality in carcinoma